Surgical Hysteroscopy
It is a narrow luminous tube with an optical instrument or visualization device at the end that is used to examine the inside of the uterus that is introduced through the vaginal canal into the uterine cavity and you can obtain the images on a screen and record them to check what has been found.
Missing DIU
Procedures in which a hysteroscope can be used
Endometrial ablation
It is the removal of the endometrium (thin layer that lines the uterus inside). It is an alternative to hysterectomy in women with heavy bleeding who do not want to undergo the removal of the uterus; With this procedure, the patient stops bleeding or has a minimal menstrual bleeding with a high degree of satisfaction; The ovaries are preserved and they continue to function and produce the female hormone that avoids the symptoms that occur when the uterus is removed. It is also used to control bleeding in post-menopausal women.

Instrumentation for hysteroscopic surgery
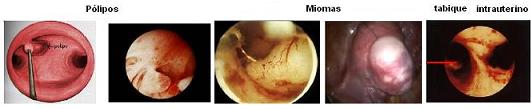
Polypectomy
We proceed to the removal of polyps that are small fleshy formations that give abundant bleeding are usually of benign origin and are extracted from the interior of the uterine cavity through a small outpatient surgery, getting back to having normal menses in most cases.
Polypectomy
Removal of foreign bodies
It is used to locate lost devices that do not have the guide wires or that are out of their usual place; With a small clamp that enters through the cervix and with direct hysteroscopic vision can be extracted.
Release of adhesions or intrauterine partitions
Some women have malformations in the form of partitions inside the uterine cavity and that can cause abortions to repeat or sterility, they can be removed without the need of the usual open surgery, as well as the intrauterine adhesions or synechiae can be released.
Myomectomy
It consists of the removal of benign tumors that grow from the uterine muscle into the uterine cavity or protrude outside the uterine musculature; they can generate abundant bleeding and sometimes cause repeated abortions, they are extracted with a thin instrument called resectoscope or morcellator that are part of the new hysteroscopic techniques or by small wounds in the abdomen if the case so deserves with the object of preserving the uterus.
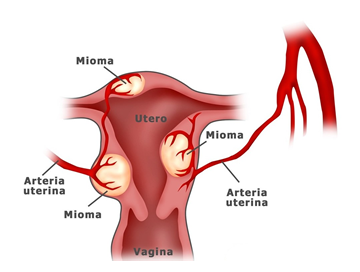
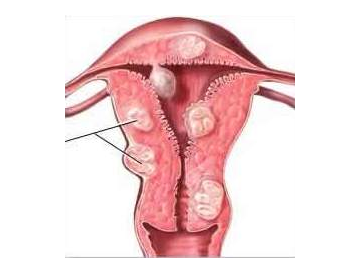
Myoma of the uterine body
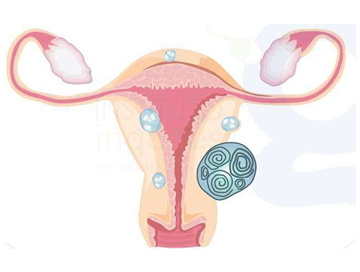
Location sites of uterine myomas