Prevention of HPV (Human Papilloma Virus)
The term known as condylomata, genital warts or HPV / HPV (represents the acronym of the human papilloma virus) or virus causing injuries that affect the skin and mucous of animal species and also man.
It is an infection caused by a virus that has many subgroups and some of these can be the cause of injuries that could lead to cancer of the cervix and genital warts.
In recent times, the interest of the general public in learning more about this type of infection that can cause dysplastic lesions at the level of the cervix, the vagina or warts in the skin of the ano-perineal region, of the penis has taken an important turn. , of the oral mucosa and of the oro-pharynx. It is important to clarify that the pap smear or paptest is not a conclusive test to identify the virus, or if the cervical cells are infected. Only 60% of cases can come out positive; sometimes, neither the same colposcopy (amplification of the images) of the cervix and the vaginal mucosa is sufficient to discover the degree of involvement of this type of cells of the cervix and a biopsy is required to be confirmed by part of the pathologist, if there is a viral infection.
At present it has been seen that there are several subtypes of viruses that can cause injuries but above all, subtypes are mentioned. 6, 11, 14, 16, 18, 31, 33, 35, 39, 44, 45, 52, 55, 56 , 58, 59, 67, 74, 81, 84, 85 but in our country we do not have very well defined statistics of the most frequent subtypes, although the respective hydration studies are already being carried out to determine the type of high-grade virus oncogenic or low grade.
The new tetravalent vaccine, and lately, there is a nonavalent vaccine that is already available in our environment could prevent the future transmission of subtypes 6,11,16 and 18 with the prophylactic administration of three doses, it should be emphasized that the vaccine does not cure the lesions, the same ones that have to be extirpated or fulgurated to get them to disappear.
H.P.V (Condolimatosis or Genital Warts)
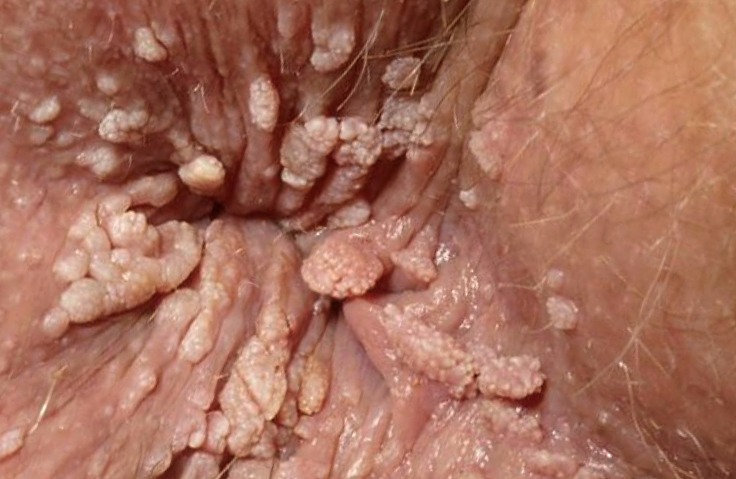
Condyloma Anal
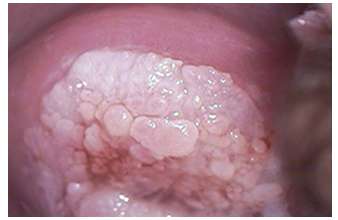
Cervical Condyloma
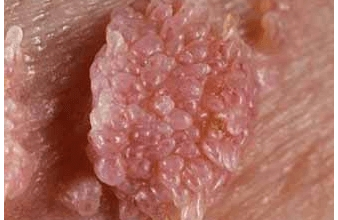
Condyloma Vaginal Mucosa
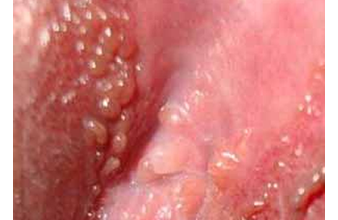
Vulvar condyloma.
At the beginning of the first application, it would be counted as day 1 (first dose) at 60 days the second dose would be placed and at 180 days, that is, at 6 months (third dose), with this the scheme would be completed total vaccination and it could be established that the person who did so is protected.
Boys and girls from 10 years of age until they are around 45 years old and preferably have not had previous exposure or contagion with the virus; since the vaccine does not serve to cure or eliminate the lesions that appear as a result of the infection; or if they have already had the contagion, they would be protected against the types of virus that cause this type of infection, and it has been seen that cross-protection occurs with the other subtypes that persist over time.
Vaccination is done by placing an intramuscular injection into the deltoid muscle, near the shoulder, usually without pain or adverse post-vaccinal reactions. The use of this vaccine has been approved by the FDA until the age of 45, in men and women: The earlier the three doses of the vaccine are placed the greater the immunity or protection produced by the vaccine. The administration of this vaccine should not be done indiscriminately or by self-medication, but should be prescribed under the supervision of the appropriate medical professional, be it pediatrician, internist or gynecologist.
A conservative procedure is performed that removes or flares the verrucous lesions at the level of the skin of the perineum and vulva or in case of uterine cervix lesions; A small portion of the cervix (leep cone) is removed when there is an infection caused by the human papillomavirus (HPV) and which sometimes causes alarm; because many women undergo hysterectomies; how well they could have been avoided and even maintain the possibility of getting pregnant; without any risk to the baby.
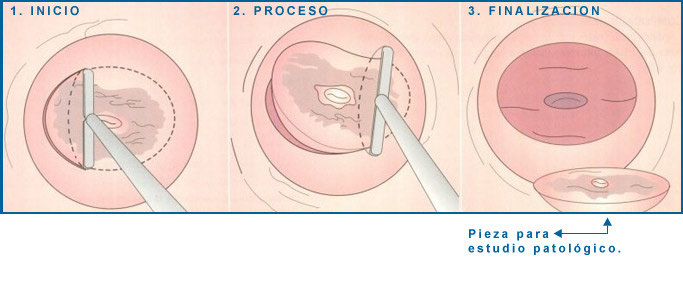
Cervical Conization
By means of a radiofrequency technique (CONE LEEP), similar to the laser, the most external part of the cervix is removed in cases where the cells are infected by the HPV Virus (Human Papilloma Virus, which causes cancer of the uterus). cervix), without having to perform the hysterectomy (removal of the uterus). With the possibility of getting pregnant again.
Pasos para la conización